Blog for Respiratory-Medicine-Post-Graduates of Apollo Hospitals,Chennai,India - Diplomate National Board(DNB), started in the Year 2009 October ,by PGs & the Academic Co-Ordinator of Department - Dr.R.P.Ilangho - for enabling these Young PGs to INTER_CONNECT ideally for becoming better Pulmonologists.The word~ REMAP09 ~ was coined thus:RE= RE spiratory M=M edicine A=Apollo P= P ostGraduate 09= 2009 - thus meaning "Respiratory Medicine Apollo PostGraduate 2009 batch"
Snap Your Fingers ! Slap Your face ! & Wake Up !!!
FUN is the most Sacred Word in all the religious texts put together - in Life !
Snap Your Fingers ! Slap Your Face ! & Wake Up !!!
Labels
- .ATS GUIDELINES OF TB DEFAULT AND RELAPSE (1)
- 1.WHY FASCIAL PUFFINESS OCCURS FIRST IN RENAL EDEMA (1)
- Acute (2)
- ACUTE EXACERBATION OF COPD CRITERIA (2)
- ACUTE EXACERBATION OF ILD CRITERIA (1)
- ACUTE EXACERBATION OF IPF criteria (1)
- AE COPD (1)
- Air crescent sign and Monod sign (1)
- Alveolar arterial oxygen gradient (1)
- Aminophylline in asthma (1)
- Amphoric breathing (1)
- Anuria and oliguria definition (1)
- apical cap (1)
- Apical impulse (1)
- Assessment of respiratory muscle strength (1)
- Asthma PEF variablity (1)
- Att in hepatotoxicity (1)
- ATT weight band recent (1)
- Austin flint murmur and Graham steel murmur (1)
- BEQ (1)
- Berryliosis causes (1)
- BMI (1)
- Borg dyspnoea score (1)
- Breathlessness - Aggravating relieving factors (1)
- breathlessness-sherwood jones (1)
- Bronchiectasis- Definition (1)
- BRONCHOPULMONARY SEGMENTS (1)
- Cardinal symptoms: aggravating and relieving facto (1)
- Cardinal symptoms: aggravating and relieving factors (1)
- Causes of chest pain aggrevated by cough (1)
- Causes of localised bulging of chest wall (1)
- Causes of orthopnea (1)
- Causes of palpitation (1)
- Causes of Unilateral pedal edema (1)
- Cavity (1)
- check post (1)
- Chest physiotherapy (1)
- Chromogranin A (1)
- Chronic (2)
- Classification (1)
- Clinical features of different stages of syphilis (1)
- Clubbing (1)
- clubbing -mechanism of (1)
- Clubbing Unilateral (1)
- CLUBBING-PATHOGENESIS PDGF (1)
- cobb's angle-In Kyphoscoliosis Cobb's angle above which can be operated (1)
- Cobbs angle (1)
- Complications of Tuberculosis (1)
- Conditions causing Concave st segment elevation (1)
- Cor pulmonale (1)
- Cough reflex (2)
- Cough- aggravating factors (1)
- Cultures- significant colony count (1)
- Cyst/Bulla/Bleb (1)
- Cystic Fibrosis- Female infertility (1)
- DD of Orthopnoea (1)
- definition (1)
- DNB question bank (1)
- Dog related infections of the lung (1)
- Drugs causing breathlessness (1)
- dysphagia - approach (1)
- Dyspnea - Causes of acute dyspnea (1)
- ECG FEATURES OF DEXTROCARDIA (1)
- Emphysema (1)
- Emphysema and chronic bronchitis definition (1)
- Empyema necessitans (1)
- Exacerbation of ILD (1)
- Factitious asthma (1)
- Familial ILD differential diagnosis (1)
- Fever of unknown origin (1)
- fibrinolytics in plef (1)
- FORMOTEROL (1)
- Gastro Intestinal Tract and abdominal symptoms (1)
- GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM - SYMPTOMS (1)
- Gram negative cocci & gram positive bacilli (1)
- HAM (1)
- Hemothorax (1)
- Honeycombing in HRCT (1)
- Hydropneumothorax- sound of Coin test (1)
- Hyperventilation syndrome (1)
- IDSA sinusitis management (1)
- ILD CLASSIFICATION (1)
- ILO classification for pneumoconiotic opacities (1)
- Impalpable apical impulse (2)
- INDICATIONS FOR NIV IN COPD (1)
- Indications for steroids in Sarcoidosis (2)
- Krogg constant (1)
- lateral winging of scapula (1)
- Lung areas sensitive to pain (1)
- lung cancer- age group (1)
- Lung cancers-ALK inhibitors (1)
- MARKERS OF ILD (1)
- Massive hemoptysis (1)
- Massive hemoptysis criteria (1)
- Mines in Tamil Nadu (1)
- Muscles of respiration (2)
- Name reason for Potts spine (1)
- Nephrotic syndrome (1)
- NORMAL BREATH SOUNDS - mechanism (1)
- NORMAL THYMUS IN CT (1)
- NYHA (1)
- Occupational hazards in Asansol (1)
- Orthopnea (1)
- Orthostatic hypotension (2)
- Overcrowding (1)
- PAH - symptoms and signs (1)
- Pain- CRPS (1)
- Paracetamol -MOA (1)
- Parapneumonic effusion - classification (1)
- Pathophysiology of breath sounds (1)
- Pedal edema Aggravating and relieving factors (1)
- Penetration and exposure in Chest Xray (1)
- Perception of Dyspnoea (1)
- Pleuroscopy guidelines (1)
- PND causes (1)
- Pneumatocele (1)
- pneumonia phases of (1)
- Positional variation in chest pain (1)
- Post tussive suction (1)
- PPF criteria (1)
- Puddle sign (1)
- Pulmonary embolism (1)
- Pulsations in different areas- causes (1)
- Pulsus paradoxus (1)
- Pulsus paradoxus - Measuremen (2)
- RADS-Definition and Criteria (1)
- Respiratory system clinical examination (1)
- Rheumatoid arthritis - diagnostic criteria (1)
- S3 (1)
- S4 HEART SOUNDS (1)
- Serum cortisol (1)
- Sherwood jones classification (1)
- Shivering (1)
- Silhouette sign (1)
- Six minute walk test (1)
- Sjogren's syndrome (1)
- Skodaic resonance (1)
- SLE Criteria (1)
- Sleep study and polysomnography (1)
- Spinoscapular distance (1)
- Split pleura sign (1)
- Subacute (2)
- Subpulmonic effusion (1)
- Surface anatomy -right minor fissure (1)
- Swellin (1)
- SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS - Diagnostic criteria (1)
- Terminal respiratory unit (1)
- Test (1)
- Tidal percussion (1)
- Tongue in HIV (1)
- Upper respiratory tract (1)
- Velcro crackles (1)
- Vesicular breath sounds - Physiology (1)
- weight loss (1)
- West bengal (1)
Labels
.ATS GUIDELINES OF TB DEFAULT AND RELAPSE
(1)
1.WHY FASCIAL PUFFINESS OCCURS FIRST IN RENAL EDEMA
(1)
Acute
(2)
ACUTE EXACERBATION OF COPD CRITERIA
(2)
ACUTE EXACERBATION OF ILD CRITERIA
(1)
ACUTE EXACERBATION OF IPF criteria
(1)
AE COPD
(1)
Air crescent sign and Monod sign
(1)
Alveolar arterial oxygen gradient
(1)
Aminophylline in asthma
(1)
Amphoric breathing
(1)
Anuria and oliguria definition
(1)
apical cap
(1)
Apical impulse
(1)
Assessment of respiratory muscle strength
(1)
Asthma PEF variablity
(1)
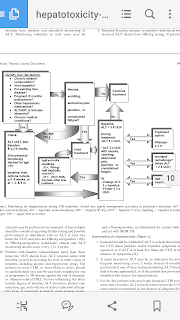
Att in hepatotoxicity
(1)
ATT weight band recent
(1)
Austin flint murmur and Graham steel murmur
(1)
BEQ
(1)
Berryliosis causes
(1)
BMI
(1)
Borg dyspnoea score
(1)
Breathlessness - Aggravating relieving factors
(1)
breathlessness-sherwood jones
(1)
Bronchiectasis- Definition
(1)
BRONCHOPULMONARY SEGMENTS
(1)
Cardinal symptoms: aggravating and relieving facto
(1)
Cardinal symptoms: aggravating and relieving factors
(1)
Causes of chest pain aggrevated by cough
(1)
Causes of localised bulging of chest wall
(1)
Causes of orthopnea
(1)
Causes of palpitation
(1)
Causes of Unilateral pedal edema
(1)
Cavity
(1)
check post
(1)
Chest physiotherapy
(1)
Chromogranin A
(1)
Chronic
(2)
Classification
(1)
Clinical features of different stages of syphilis
(1)
Clubbing
(1)
clubbing -mechanism of
(1)
Clubbing Unilateral
(1)
CLUBBING-PATHOGENESIS PDGF
(1)
cobb's angle-In Kyphoscoliosis Cobb's angle above which can be operated
(1)
Cobbs angle
(1)
Complications of Tuberculosis
(1)
Conditions causing Concave st segment elevation
(1)
Cor pulmonale
(1)
Cough reflex
(2)
Cough- aggravating factors
(1)
Cultures- significant colony count
(1)
Cyst/Bulla/Bleb
(1)
Cystic Fibrosis- Female infertility
(1)
DD of Orthopnoea
(1)
definition
(1)
DNB question bank
(1)
Dog related infections of the lung
(1)
Drugs causing breathlessness
(1)
dysphagia - approach
(1)
Dyspnea - Causes of acute dyspnea
(1)
ECG FEATURES OF DEXTROCARDIA
(1)
Emphysema
(1)
Emphysema and chronic bronchitis definition
(1)
Empyema necessitans
(1)
Exacerbation of ILD
(1)
Factitious asthma
(1)
Familial ILD differential diagnosis
(1)
Fever of unknown origin
(1)
fibrinolytics in plef
(1)
FORMOTEROL
(1)
Gastro Intestinal Tract and abdominal symptoms
(1)
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM - SYMPTOMS
(1)
Gram negative cocci & gram positive bacilli
(1)
HAM
(1)
Hemothorax
(1)
Honeycombing in HRCT
(1)
Hydropneumothorax- sound of Coin test
(1)
Hyperventilation syndrome
(1)
IDSA sinusitis management
(1)
ILD CLASSIFICATION
(1)
ILO classification for pneumoconiotic opacities
(1)
Impalpable apical impulse
(2)
INDICATIONS FOR NIV IN COPD
(1)
Indications for steroids in Sarcoidosis
(2)
Krogg constant
(1)
lateral winging of scapula
(1)
Lung areas sensitive to pain
(1)
lung cancer- age group
(1)
Lung cancers-ALK inhibitors
(1)
MARKERS OF ILD
(1)
Massive hemoptysis
(1)
Massive hemoptysis criteria
(1)
Mines in Tamil Nadu
(1)
Muscles of respiration
(2)
Name reason for Potts spine
(1)
Nephrotic syndrome
(1)
NORMAL BREATH SOUNDS - mechanism
(1)
NORMAL THYMUS IN CT
(1)
NYHA
(1)
Occupational hazards in Asansol
(1)
Orthopnea
(1)
Orthostatic hypotension
(2)
Overcrowding
(1)
PAH - symptoms and signs
(1)
Pain- CRPS
(1)
Paracetamol -MOA
(1)
Parapneumonic effusion - classification
(1)
Pathophysiology of breath sounds
(1)
Pedal edema Aggravating and relieving factors
(1)
Penetration and exposure in Chest Xray
(1)
Perception of Dyspnoea
(1)
Pleuroscopy guidelines
(1)
PND causes
(1)
Pneumatocele
(1)
pneumonia phases of
(1)
Positional variation in chest pain
(1)
Post tussive suction
(1)
PPF criteria
(1)
Puddle sign
(1)
Pulmonary embolism
(1)
Pulsations in different areas- causes
(1)
Pulsus paradoxus
(1)
Pulsus paradoxus - Measuremen
(2)
RADS-Definition and Criteria
(1)
Respiratory system clinical examination
(1)
Rheumatoid arthritis - diagnostic criteria
(1)
S3
(1)
S4 HEART SOUNDS
(1)
Serum cortisol
(1)
Sherwood jones classification
(1)
Shivering
(1)
Silhouette sign
(1)
Six minute walk test
(1)
Sjogren's syndrome
(1)
Skodaic resonance
(1)
SLE Criteria
(1)
Sleep study and polysomnography
(1)
Spinoscapular distance
(1)
Split pleura sign
(1)
Subacute
(2)
Subpulmonic effusion
(1)
Surface anatomy -right minor fissure
(1)
Swellin
(1)
SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS - Diagnostic criteria
(1)
Terminal respiratory unit
(1)
Test
(1)
Tidal percussion
(1)
Tongue in HIV
(1)
Upper respiratory tract
(1)
Velcro crackles
(1)
Vesicular breath sounds - Physiology
(1)
weight loss
(1)
West bengal
(1)
Search This Blog
Pages
Sunday, March 18, 2018
Friday, March 9, 2018
High attenuation mucous
HIGH ATTENUATION MUCOUS PLUG:
ACCORDING TO RITESH AGARWAL Et. al,
High attenuation mucus means - Radiologically > 70 HU .
Reference
ACCORDING TO RITESH AGARWAL Et. al,
High attenuation mucus means - Radiologically > 70 HU .
Reference
High-Attenuation Mucus Impaction in Patients With Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: Objective Criteria on High-Resolution Computed Tomography and Correlation With Serologic Parameters.
(PMID:26323654)
Abstract
The aim of the study was to correlate the high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) finding of high-attenuation mucus (HAM) impaction, including mean CT density and immunologic parameters in patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA). The institutional review board approved the study, and informed written consent was obtained. A total of 100 consecutive patients diagnosed with ABPA between June 2012 and December 2013 undergoing HRCT were enrolled. HRCT scan of the chest was evaluated for central bronchiectasis, mucoid impaction, and number of involved bronchial segments. Findings of mucoid impaction in patients were classified as HAM and non-HAM. CT attenuation values and mean CT density were calculated. Serologic parameters were assessed for total immunoglobin E (IgE), specific IgE, and absolute eosinophil count. Patients with HAM impaction on HRCT were found to have significantly higher levels of total IgE (P < 0.001), specific IgE (P = 0.03), and number of bronchial segments affected (P < 0.001). We found a CT density value of 70 Hounsfield units (HU) as an adequate cutoff value for HAM impaction. CT density >100HU is correlated with significantly higher values of serologic parameters. The present study suggests a relation between absolute HU values of HAM impaction and absolute value of serologic parameters in ABPA.
Thanks
Govind
Tuesday, March 6, 2018
Monday, March 5, 2018
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)